Pathology and Etiology
Hemorrhoids or hemis are best described as smooth lumps or swollen vessels on the upper or lower side of the first ring. They can be small or large, hard or soft, painful or painless, temporary or long-lasting[1], shallow or deep (relatively speaking), and may or may not bleed when pressed/squeezed.
They occur when weak or damaged tissue within an area known as the hemorrhoidal plexus cannot fully support blood vessels. As a result, blood vessels will expand with excess blood which causes swelling. The swollen vessel will cause intense pain in external hemorrhoids but will likely be painless in internal hemorrhoids[2].
Thinner tissue around upper hemorrhoids means they are more likely to break and bleed when pressure is applied.
VOCABULARY
Hemorrhoidal Plexus
- Noun A dense network of veins within the anus that creates a seal which prevents continual escape of gas or liquids from the rectum. The plexuses are also responsible for rectal/anal blood drainage.


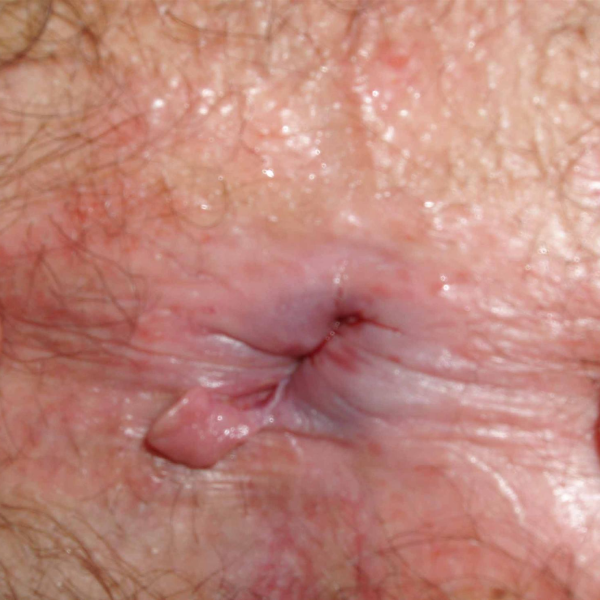
Figure 1.1 [ A - B ]: Healthy and Damaged Hemorrhoidal Plexuses
[ A ] The veinous networks encircling the hole are known as hemorrhoidal plexuses. [ B ] An engorged vein within a plexus will result in an internal or external hemorrhoid.
Bleeding or painful hemorrhoids may prevent fucking, toy play, fisting and sometimes sitting.
In the medical world, hemorrhoids and classified as:
- External | Occurring below the Dentate Line in the Inferior Hemorrhoidal Plexus. This is a technical way of saying they are shallow and appear around the rim of the hole. They can usually be seen and felt, but in some cases, a swollen hole may disguise the hemi.
- Internal | Occurring deeper inside the hole, above the Dentate Line in the Superior Hemorrhoidal Plexus. Internal hemorrhoids are staged as follows[3]:
-
- Grade I / Mild | Does not protrude beyond anal canal (non-visible).
- Grade II / Moderate | Protrudes during defecation or fisting but retracts into the hole without assistance.
- Grade III / Significant | Prolapses during defecation or fisting and must be manually pushed back into the hole.
- Grade IV / Extreme | Permanently prolapses and does not retract under any circumstance.
In addition to external and internal classifications, hemorrhoids can have these characteristics:
- Thrombosed | Filled with clotted blood with a blue, purple, or white coloration, typically associated with external hemorrhoids.
- Prolapsed | Bulging internal plexus tissues and veins that have dropped or descended outside the hole itself.
- Bleeding | Draining blood when subjected to pressure (such as fisting or bowel movements).
Hemorrhoids can also be categorized as:
- Acute | Short-lived, usually healing within a few days or as long as six weeks.
- Chronic | Long-lasting, usually taking a few months or even a year to heal, with reoccurrence in the same location common.
Injury Indices
Damage to Fist Chute
Low
Although hemorrhoids may temporarily affect bottoming, it is rare to experience permanent damage.
Surgical and non-surgical methods can be used to resolve hemorrhoids. Surgical interventions can cause significant damage to the fist chute and affect the ability to bottom.
Life-threatening Injury
Extremely Low
Neither acute nor chronic hemorrhoids result in loss of life.
Extremely rare reports of anemia and sepsis have been linked to severe bleeding. Untreated sepsis is life threatening.
Probability of Condition
High
Most fisters will experience hemorrhoids in their lifetime regardless of experience level. Hemorrhoids are more likely with insufficient lubrication, extreme fisting (punch or width), heavily textured toys, virgins, or novice fisters.
In some men, gentle fisting or soft toy play can alleviate symptoms. In others, any ass play makes symptoms worse.